June 4 2025 – The e-Motor Rotor Temperature Sensor (eRTS) technology offers a completely new way to measure heat in permanent magnet synchronous electric vehicle (EV) motors, resulting in many advantages for OEMs. It is one of several sensor technologies for electric vehicles developed by the product center “E-Mobility-Sensors” (EMS) at Continental Automotive.
Since the temperature inside electric vehicle (EV) motors can reach up to 150 degrees Celsius, heat management is crucial to prevent the rotor magnet from demagnetization due to excessive temperature. Current solutions do not measure heat development directly, but calculate it based on the information from the stator temperature sensor, phase current measurements and environmental variables. The eRTS technology measures heat development directly inside the EV motor near the temperature origin, resulting in a much higher accuracy of the reported temperature: current solutions report the temperature with a tolerance of 15 degrees Celsius, whereas the eRTS sensor measurement is specified to an accuracy with three degrees tolerance.
Therefore, car manufacturers benefit from new possibilities and freedom of choice in permanent magnet synchronous EV motor design: eRTS technology enables a more cost-efficient use of rare earth elements used to protect the rotor magnet. Another interesting variable is the possibility to improve motor performance by pushing the limits of the tolerance range. In combination with other sensor technologies, it can even act as a system solution to create synergies that can save car manufacturers money and effort.
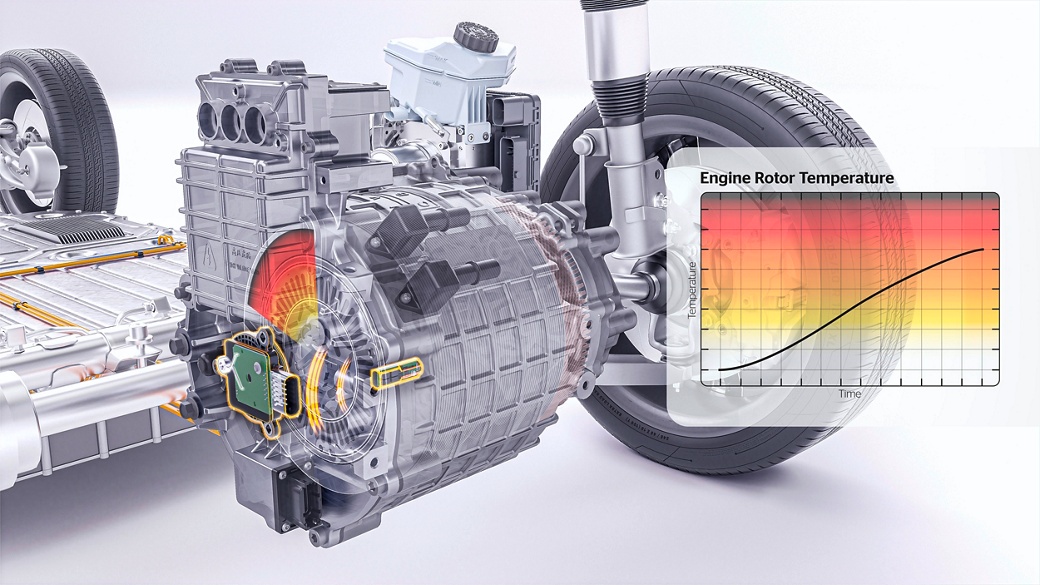
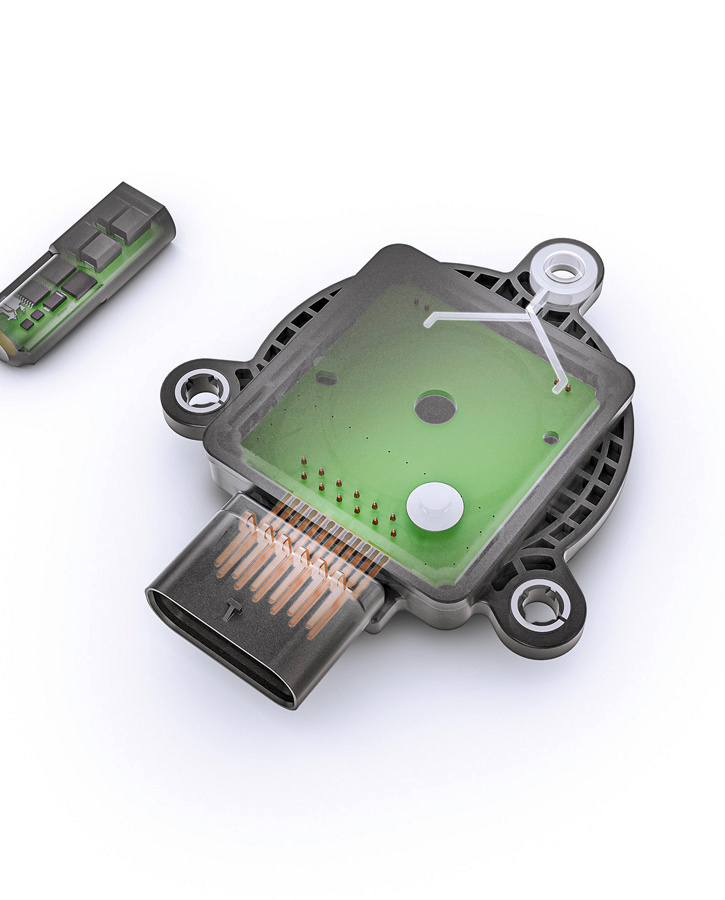
eRTS contains two separate components, the mote element and the transducer element. The mote temperature sensor unit measures the temperature directly at the target area as close as possible to the magnet in the rotor. The wireless mote draws its energy only from the wired transducer that is connected to the ECU, providing the transducer with its measuring data. The transducer is located outside the EV motor on the chassis. It is connected to the inverter control, transmitting temperature information through a communication interface. Mote and transducer communicate via Piezo ultrasound, which also provides for the energy supply.
eRTS is one of several sensor technologies for electric vehicles developed by the product center “E-Mobility Sensors” (EMS). This product center has been dedicated specifically to this area more than two years, resulting in a fast-growing portfolio of sensors specifically for EV. It is part of the Segment Passive Safety and Sensorics (PSS) at Continental’s group sector Automotive. PSS has a long tradition of sensor technologies, offering an extensive sensor portfolio of around fifty different sensors for a multitude of purposes.
“With less resource consumption and lower costs, our eRTS sensor technology is advantageous to current solutions. This innovation shows that investing and focusing expertise in our product center were the right decision. We will further continue this path and expand our portfolio of sensors for EVs successively,” says Bin Huo, Head of the Passive Safety and Sensorics Segment (PSS) at Continental Automotive.
